

When many people think of the terms:
they often don’t realise that they each have important differences that set them apart from each other.
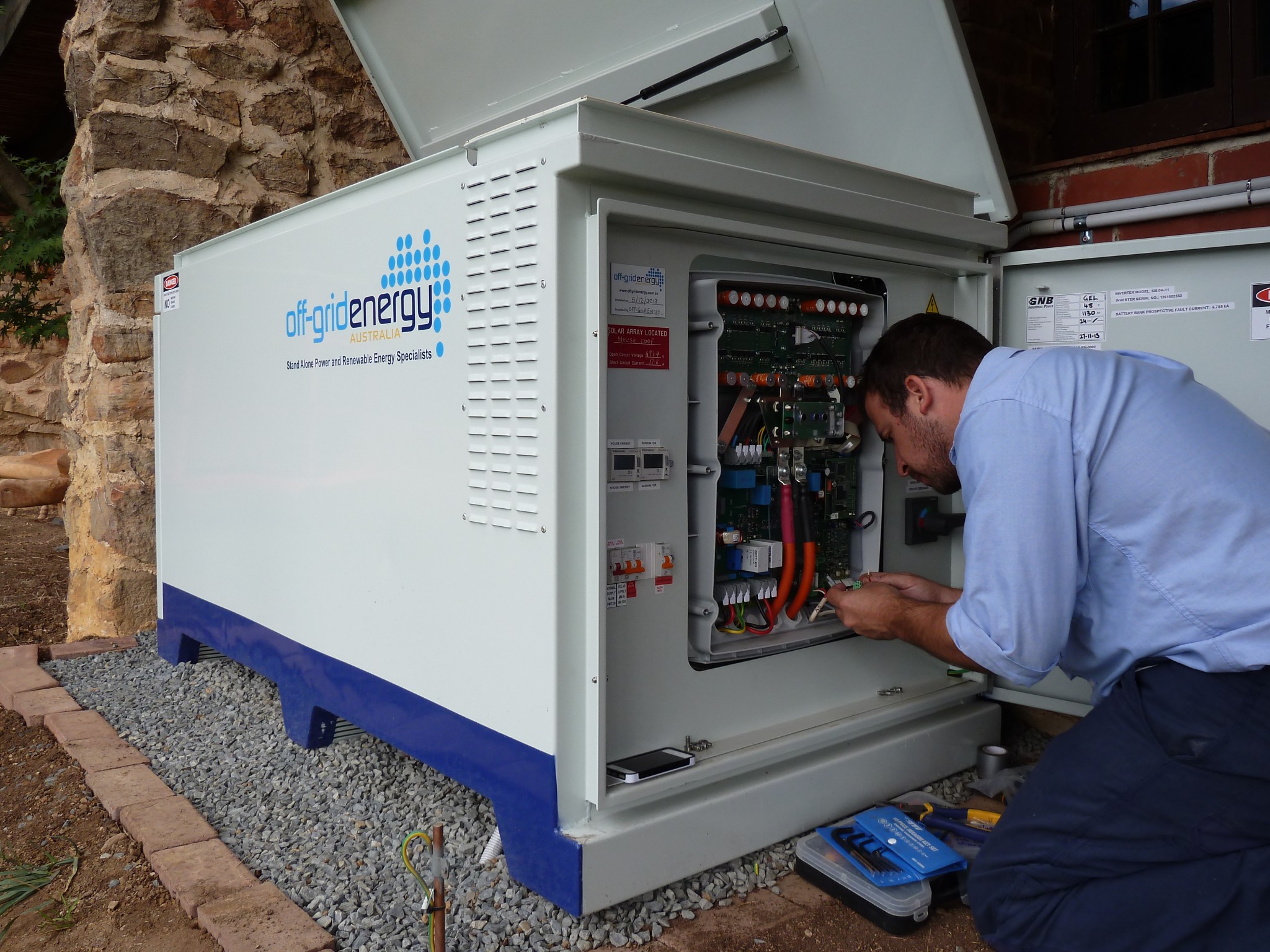
Refers to a system uniquely designed to power any application that is not connected to the public utility grid. In such situations there is very little scope for compromise in the system design, as energy security and reliability are paramount.
It’s important that the battery storage capacity in off-grid applications includes a comfortable level of ‘Autonomy’. What this means in practice, is that off-grid systems need larger ‘useable’ storage capacities to ride through periods of poor weather or increases in user demand. Off-grid systems also require larger equipment to be able to run all household appliances and loads without being overloaded.
Another key factor to remember is there is no backup should equipment fail, batteries deplete, or the backup generator not start. Your supplier essentially becomes your electricity retailer, so choosing the right supplier is important.
Refers to properties that have grid electricity connected but also have a level of battery storage. Typically batteries are used to store excess solar from a grid connected solar system for use at night.
The ability to store solar energy rather than selling it to the grid at a reduced feed-in-tarrif (FIT) is becoming an increasingly popular concept, as the wave of unhappy electricity consumers protest against the large electricity companies and rising costs.
Grid-tied storage can range greatly in size and capability.
Refers to uninterrupted power supplies (UPS) which provide a level of power in blackout or power failure situations – usually to a nominated appliance/s or load/s. The battery storage can be charged via the electrical grid, solar or fuel generators and the system will sit idle until there is power failure.
These systems are most common for communication and IT equipment, as any power interruptions can cause big issues. For households, battery backup features can now often be incorporated into certain grid storage systems.



Powering the Future: How Digital Technologies Have Revolutionised Off-Grid Power Systems In the pursuit of a sustainable future, the energy sector has witnessed remarkable advancements

Do you wish you never had to suffer another blackout ever again? It sounds too good to be true, but for many people, this dream is becoming a reality.

Australia will be one of the first countries to receive the much anticipated Powerwall. Here’s the details on what it means for your home’s solar system.

Off-Grid Energy is proud to have been selected as both an Authorised Reseller and Certified Installer for Tesla, and also been chosen as one of the first Authorised Installers for Redflow’s ZCell.
Electrical Contractor Licenses: VIC REC-31913, TAS 15608294, WA EC15901, SA PGE278927, NSW 279181C
We acknowledge the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and recognise their continuing connection to land, waters and culture. We would like to specifically acknowledge the Kaurna, Wathaurong, Wonnarua, Wiradjuri and Boonwurrung people. We pay our respects to their Elders past, present and emerging.